
The Concentration Versus Time Plotįrom the concentration versus time plot, a pharmacokineticist can begin to understand the absorption and elimination characteristics of the drug.
#WINNONLIN 2 COMPARTMENT SOFTWARE#
Once the pharmacokineticist receives the drug concentration data, a PK software package is used to construct concentration versus time plots to graphically display the pharmacokinetics of the drug in the given matrix and to estimate relevant PK parameters. These measurements are provided to the pharmacokineticist by a bioanalytical lab, where blood or plasma samples (or other appropriate matrix samples) from study subjects are analyzed using sensitive detection techniques. PK analysis relies on observed drug concentration measurements over time in a relevant, accessible matrix (typically blood or plasma). In the real world, this approach is not practical and we must instead make estimates based upon what can be realistically measured. In an ideal world, the way a drug moves through the body could be tracked directly in every body fluid and tissue.

How is a Noncompartmental Analysis Performed? NCAs are the most commonly used approach for establishing the initial exposure characteristics of a drug prior to entry into the clinic (i.e., during nonclinical PK and toxicology studies). On the other hand, NCAs are typically favored for characterizing PK within a single study, including both final analyses and any interim analyses used to make dose escalation decisions. informing dosage adjustments based upon these factors.age, sex, race, renal impairment, hepatic impairment.exploring PK variability due to intrinsic factors and extrinsic factors.characterizing PK across multiple studies.Compartmental methods have key advantages including: When to Use Noncompartmental Analysisĭeciding whether to use a noncompartmental analysis versus a compartmental analysis approach is not a function of how sophisticated the method is but depends in large part upon the purpose of the analysis. NCAs often prove faster and more cost-efficient to conduct, especially when compared to more complex compartmental analyses (e.g., compartmental models that are applied to population PK analyses and that rely upon sparse sampling techniques). In addition, NCA relies almost exclusively upon algebraic equations to estimate PK parameters, making the analysis less complex than compartmental methods. Noncompartmental analysis (NCA) methods are model-independent, meaning they do not rely upon assumptions about body compartments, and they tend to provide more consistency. When using a compartmental approach, there is the potential for variability in the output of the analysis because the assumptions used to build the PK model may be somewhat different from one pharmacokineticist to another. Based on this view, the pharmacokineticist makes certain assumptions and develops models based upon nonlinear regression analysis to describe the PK of the drug. Compartmental AnalysisĬompartmental methods consider the body to consist of a finite number of interconnected, well-mixed, and kinetically homogeneous compartments (e.g., blood, organs, and other tissues). One is compartmental PK analysis and the other is noncompartmental PK analysis (NCA).
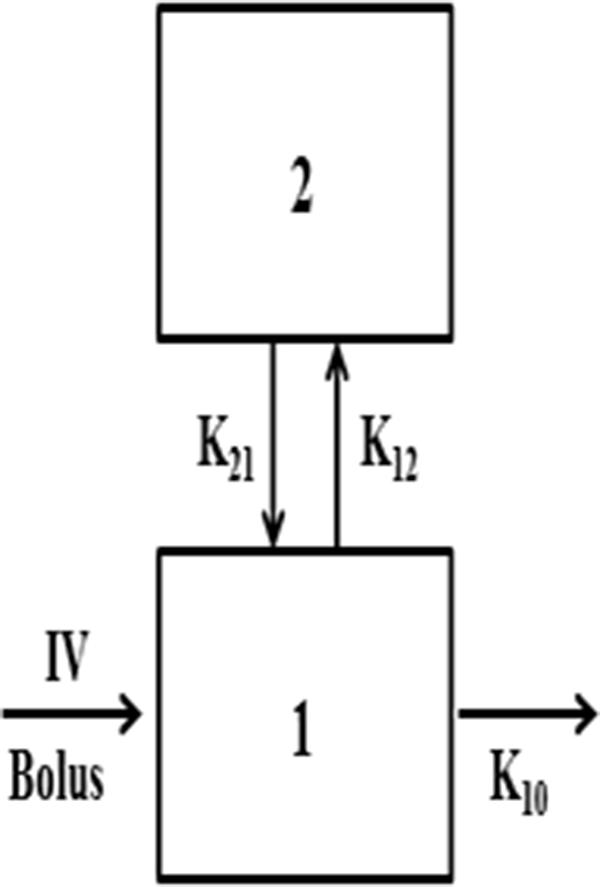
There are two common approaches to understanding a drug’s PK. Insights into a drug’s PK are used to inform the drug development program and are critical for guiding input and decision-making by regulatory authorities like the FDA.

In other words, PK is used to describe the absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion (ADME) of a drug.
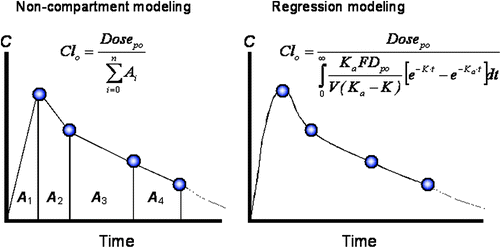
PK helps us understand how a drug moves into the body, passes through the body, and is eventually cleared from the body in a quantitative way. Pharmacokinetics (PK) is the branch of pharmacology that explores the effects of the human body on a drug.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
